Govt's Borrowing Plan for FY26
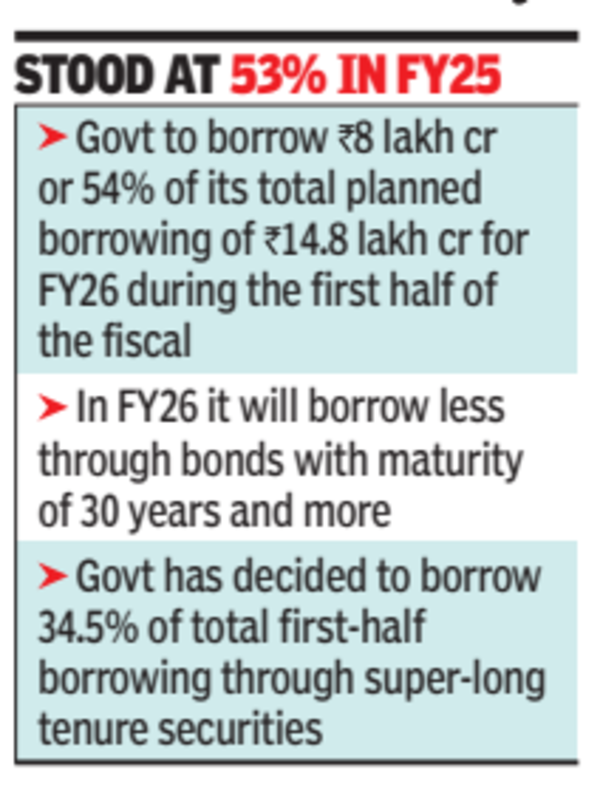
The Indian government announced its intention to borrow Rs 8 lakh crore in the first half of FY26, accounting for 54% of its annual target. This decision reflects a cautious approach to avoid pressuring interest rates upwards, especially during a period when the RBI is injecting unprecedented liquidity into the economy.

Adjustments in Borrowing Strategy
In response to market feedback, the government plans to reduce borrowing through 30-year and longer maturity bonds, citing muted demand. This adjustment is part of a broader strategy to align borrowing practices with investor appetite and current economic conditions.
Market Reactions and Expert Opinions
"The avoidance of front-loading the borrowing program is a strategic move to support growth without exerting undue pressure on market rates," noted Ram Kamal Samanta of Star Union Dai-ichi Life Insurance. This approach comes amid signs of growth moderation and aims to balance fiscal consolidation with the need for economic stimulus.
Historical Context and Future Outlook
The government's borrowing strategy has evolved over the years, with the current plan showing a slight increase in the proportion borrowed in the first half compared to FY25. The decision to adjust the mix of securities offered reflects ongoing assessments of market demand and economic indicators.









Comments